
Sep 25, 2024
Mohamed Ali Memmi
Enhancing Sustainability Through Digital Twin Technology: Simulating and Optimizing Electricity Consumption in Manufacturing
The increasing focus on sustainability has driven industries to explore innovative solutions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve energy efficiency. One significant factor contributing to a factory’s carbon footprint is electricity consumption, which varies depending on the energy source used. Our latest MVP project aims to address this challenge by simulating and calculating electricity usage throughout a production line, integrating this data into an advanced digital twin platform.
The Role of Energy in Manufacturing
Emissions by sector: Industry and electric power generation are the two largest contributors to global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, together making up nearly 60% of the global total. In 2021, both sectors accounted for 29% of global GHG emissions, with most of these emissions originating from coal combustion. Other sectors, such as land use, agriculture, and waste, collectively contributed 20%, while transportation and buildings accounted for 15% and 7%, respectively (Source: Rhodium Group, 2022).
In manufacturing, electricity consumption plays a pivotal role in determining a factory’s overall carbon footprint. Factories that rely heavily on fossil-based energy sources, such as coal, oil, or natural gas, significantly contribute to GHG emissions. However, a transition to renewable energy sources—such as hydropower, wind, or solar power—can dramatically reduce environmental impact.
Our project aims to tackle this challenge by providing real-time insights into electricity consumption, empowering manufacturers to adopt greener and more energy-efficient operations. By integrating electricity data into a comprehensive digital twin platform, we leverage IoT technology to capture and transmit real-time production data. This platform enables us to simulate and track energy usage across the entire production line, from start to finish (A to Z), with the ultimate goal of calculating and reducing climate gas emissions.

Project Overview: Integrating Energy Data into Digital Twin Platforms
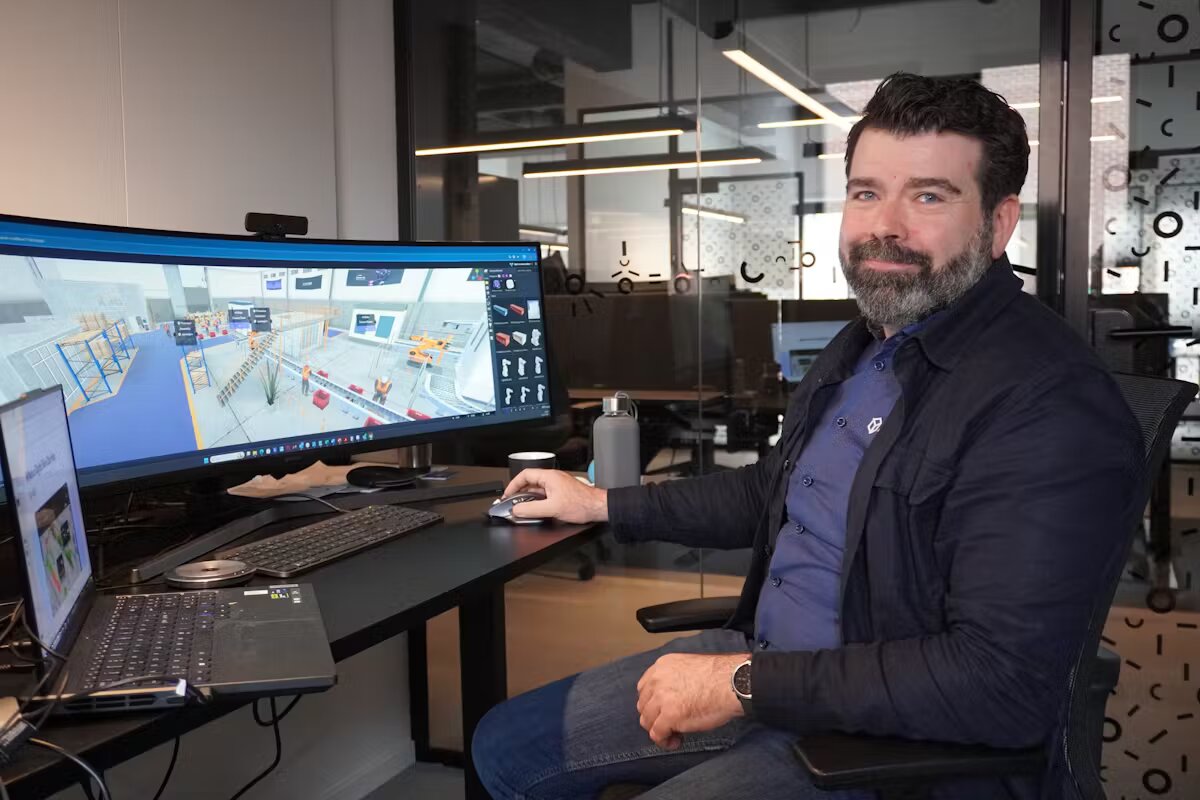
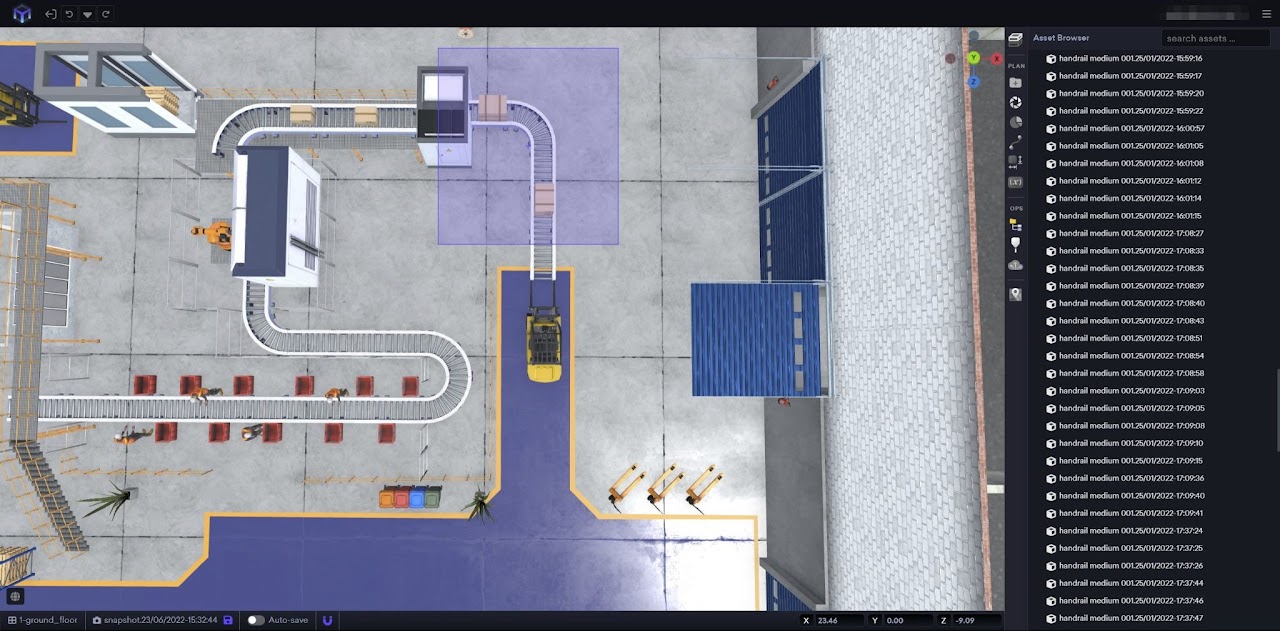
After receiving approval and funding from Grønn Fremtid Innlandet, our team embarked on this exciting MVP to enhance sustainability in manufacturing. Our objective is to simulate and measure electricity consumption throughout a production line and seamlessly integrate this data into our custom-built digital twin platform.
Leveraging IoT technology, we gather real-time data from sensors embedded across the production process. This allows for highly accurate, dynamic simulations of energy consumption patterns. By creating a digital replica of the physical production environment, our platform helps manufacturers visualize the impact of equipment performance, production schedules, and other variables on electricity use and climate gas emissions.

Hapro Electronics as Our Pilot Customer: Testing Electricity Sensors
One of the key milestones in this project is the collaboration with Hapro Electronics, our pilot customer. Both our team and Hapro Electronics’ team have been instrumental in testing electricity sensors deployed across their production line. These sensors, driven by IoT technology, continuously provide precise data on energy consumption at various stages of production.

This MVP project aims to demonstrate how our digital twin platform can calculate greenhouse gas emissions across the entire production process. While testing is still underway, early estimates suggest that even minor adjustments in production parameters—such as optimizing equipment usage or tweaking production schedules—could potentially lead to significant reductions in electricity consumption and, by extension, lower emissions. If these trends continue, they could have a substantial impact on companies seeking to enhance sustainability while maintaining operational efficiency.
The Future of Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
As industries increasingly focus on minimizing their carbon footprints, integrating real-time energy data into digital twin platforms will become an essential tool for sustainable manufacturing. Our project underscores the pivotal role that electricity data plays in optimizing energy consumption and mitigating greenhouse gas emissions.
In addition to our own innovations, we are proud to be an Autodesk Sustainability Tech Partner, further reinforcing our commitment to helping manufacturers achieve their sustainability objectives. This partnership, combined with our extensive use of IoT technology, allows us to incorporate cutting-edge innovation to drive even greater operational efficiency and environmental responsibility across the manufacturing sector.
Beyond improving energy efficiency, this MVP project aligns with broader sustainability goals by facilitating the transition away from fossil-based energy sources. By simulating various production scenarios, manufacturers can pinpoint the best strategies to reduce emissions without sacrificing productivity or profitability.
Conclusion
In partnership with Grønn Fremtid Innlandet and through close collaboration with customers like Hapro Electronics, we are thrilled to continue advancing sustainability in the manufacturing industry through our digital twin platform. This MVP project represents a key step toward developing a robust solution capable of calculating climate gas emissions across entire production lines. By integrating real-time electricity data into manufacturing processes via IoT technology, we provide manufacturers with powerful tools to make data-driven energy decisions.
The potential of this platform goes beyond energy optimization—it offers a scalable, transformative solution for industries striving to meet future sustainability standards. As we move forward, we look forward to fostering a more efficient and eco-friendly industrial landscape, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and contributing to a greener, more sustainable future for all.
References:
• Rhodium Group. (2022). Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions 2022. Retrieved from https://rhg.com/research/global-greenhouse-gas-emissions-2022/.















 Moicon Chatbot
Moicon Chatbot
